A newly discovered vulnerability in the IEEE 802.11 WiFi standard, known as CVE-2023-52424, poses significant risks to network security. This flaw, dubbed the SSID Confusion attack, allows malicious actors to trick devices into connecting to less secure networks, thereby enabling eavesdropping type of attacks.
The SSID Confusion Attack
Researchers have identified a critical design flaw in the IEEE 802.11 WiFi standard that affects all operating systems and WiFi clients, including those using WEP, WPA3, 802.11X/EAP, and AMPE protocols. The SSID Confusion attack exploits the fact that WiFi network names (SSIDs) do not require constant authentication. This loophole allows attackers to impersonate trusted network names, downgrade security settings, and intercept network traffic.
Key Points:
- Vulnerability ID: CVE-2023-52424
- Affected Systems: All WiFi clients and operating systems, including home and mesh networks
- Attack Method: Adversary-in-the-Middle (AitM) using SSID spoofing
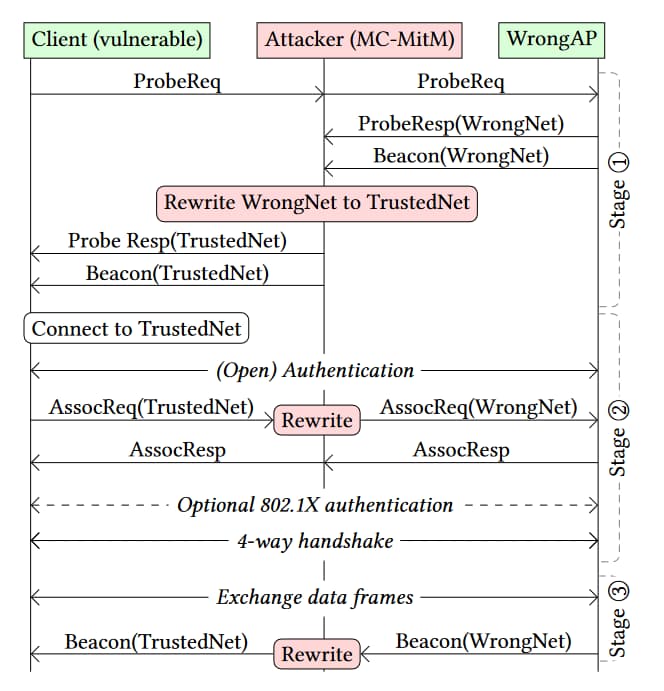
How the Attack Works
The SSID Confusion attack involves tricking a victim’s device into connecting to a rogue network with the same credentials as a trusted one. The process includes:
- Spoofing SSID: The attacker sets up a network with the same SSID as a trusted network.
- Connecting to Rogue Network: The victim’s device, believing it is connecting to a trusted network, connects to the rogue network.
- Disabling VPNs: If the VPN auto-disable feature is active, it turns off, exposing the victim’s traffic.
- Eavesdropping and Further Attacks: The attacker intercepts the victim’s network traffic and can launch additional attacks.
Impact of the Vulnerability
The SSID Confusion attack can lead to severe consequences, including:
- Exposure of Sensitive Data: Attackers can intercept confidential information.
- Security Bypass: Compromised security measures allow unauthorized access.
- Cyber Espionage: Attackers can conduct prolonged surveillance on affected networks.
Mitigation Strategies
To protect against the SSID Confusion attack, several measures are recommended:
- Update WiFi Standards: Incorporate SSID authentication as part of the 4-way handshake in the 802.11 standard.
- Enhance Beacon Protection: Allow clients to store and verify SSID authenticity using reference beacons.
- Avoid Credential Reuse: Use unique passwords for different SSIDs to prevent easy spoofing.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of security for network access.
- Regular Monitoring and Audits: Continuously monitor network activity for unusual behavior and conduct regular security assessments.
- Comprehensive Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to quickly address security breaches.
- Regular Software Updates: Ensure all devices and systems are updated with the latest security patches.
- Strong Access Controls: Implement robust access control mechanisms to limit user permissions to necessary functions only.
- Implementation of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Deploy IDS to detect and respond to unusual network activities.
Conclusion
The discovery of the SSID Confusion vulnerability in the IEEE 802.11 WiFi standard highlights the need for robust security measures to protect against emerging threats. By implementing the recommended mitigation strategies, organizations can enhance their network security and safeguard sensitive data from potential attacks. Consulting with a cybersecurity advisor or using comprehensive cybersecurity services can further strengthen your defense against such vulnerabilities.
Stay Informed: Regularly update your security protocols to ensure the safety of your network infrastructure.