Imagine opening a simple office document and unknowingly letting a computer virus into your system. Researchers at Fortinet found a seemingly normal document that was hiding a nasty surprise: a type of computer virus called FAUST ransomware. This virus is a cousin of the already known Phobos ransomware, which has been causing trouble since 2019 by locking files and asking for money to unlock them.
This time, the virus came in through a clever trick involving an office document, showing us how sneaky and dangerous these attacks can be. This FAUST version is particularly concerning because it could persist within a computer system and efficiently execute multiple tasks. Phobos ransomware has been causing destruction in the cyber world since its introduction in 2019, being involved in numerous cyberattacks. Typically, this malicious software encrypts files on a victim’s computer and then demands a cryptocurrency ransom in exchange for the decryption key. In this specific incident, the attackers utilized the Gitea service to store several files encoded in Base64 format. These files, each containing a malicious binary, trigger a file encryption attack when injected into a system’s memory.
Upon analysis by Fortinet, it was revealed that the XLAM document in question contained an embedded VBA script. When this document is opened, it activates PowerShell. Subsequently, data is downloaded from Gitea in Base64 encoding, which can be decoded to generate a clean XLSX file. This file is then automatically saved in the TEMP folder, deceiving users into thinking that the process has completed safely.
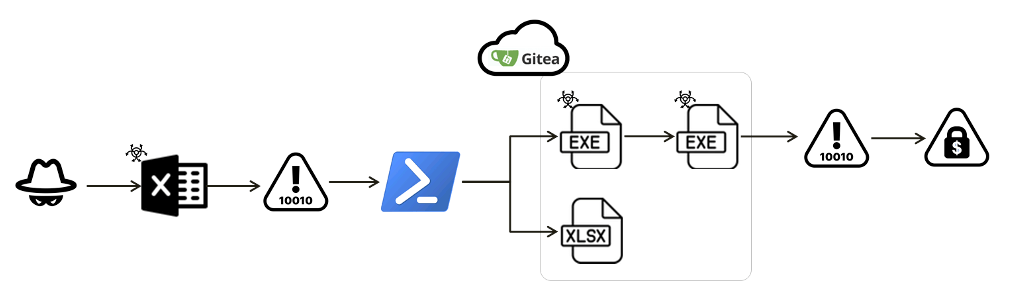
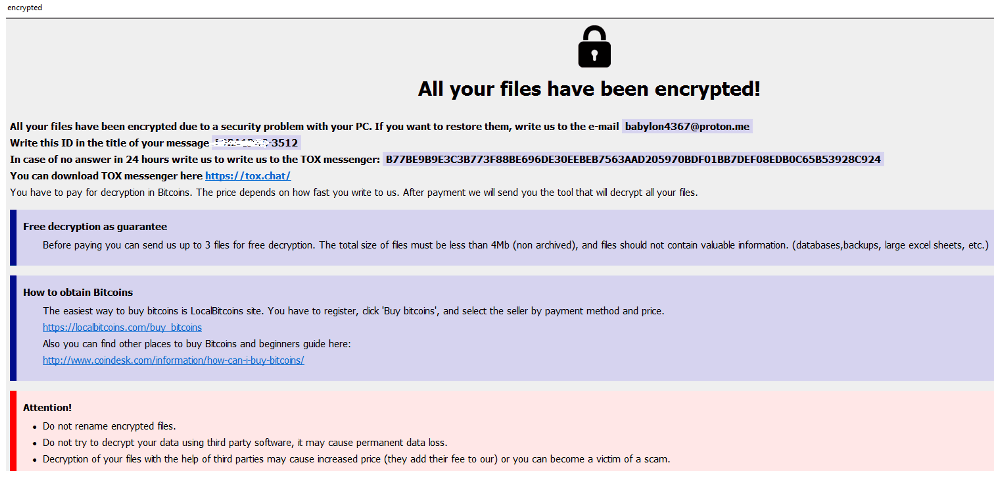
The attacker proceeds by creating a specific region of memory within the target process, inserting malicious code, and making a call to the payload’s entry point. As a result, the FAUST ransomware, a Phobos variant, adds “info.txt” and “info.hta” files to directories containing the encrypted files.
Additionally, it appends the “.faust” extension to each encrypted file. These files serve as a means for the attackers to establish contact with the victim and initiate ransom negotiations. Similar to typical Phobos versions, the FAUST ransomware also retains a decryption function for configuration purposes. Furthermore, it employs multiple threads to carry out various tasks, including deploying encryption, scanning logical drives, searching for network and sharing resources, scanning individual files, and specifically seeking database-related files.
To protect against FAUST ransomware and similar cyber threats, it’s crucial to adopt a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity. Here are some effective preventative measures:
- Educate and Train Users: The first line of defense against ransomware is awareness. Regularly educate employees about the dangers of opening attachments or clicking links in emails from unknown or untrusted sources. Conduct phishing simulations to train users to recognize suspicious emails.
- Update and Patch Systems and Applications: Keep all software, especially operating systems and applications, up to date with the latest patches. Attackers often exploit known vulnerabilities that patches have already fixed.
- Use Endpoint Solutions such as XDR and MDR: Install and maintain reputable Extended Endpoint Detection and Response solutions on all devices.
- Implement Robust Email Security: Use advanced email filtering solutions that can detect and block phishing emails, malicious attachments, and links before they reach the user’s inbox.
- Restrict Macro Scripts: Disable macros in Microsoft Office documents for users who do not need them for their daily tasks. If macros are necessary, use trusted locations or digital signatures to manage their execution.
- Use Application Whitelisting: Allow only authorized applications to run on network devices. This can prevent ransomware and other malicious software from being executed.
- Segment Networks: Divide the network into segments, limiting the spread of ransomware if it does manage to infiltrate. Ensure that sensitive information is stored in secure segments with strict access controls.
- Implement Strong Access Controls: Use the principle of least privilege for file, directory, and network share permissions. If a user or application does not need access to specific data, they should not have permission to access it.
- Monitor and Respond: Continuously monitor the network for suspicious activities and have a response plan in place. Quick isolation of infected systems and execution of the response plan can significantly reduce the impact of a ransomware attack.
By integrating these preventative measures, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to FAUST ransomware and similar cyber threats, safeguarding their data and systems against unauthorized access and encryption.
About Purple Shield Security
Purple Shield Security is not your typical cyber security consulting firm. We are the guardians of your digital realm, committed to protecting your business from the constantly evolving landscape of cyber threats. With a dedicated team of passionate security professionals by your side, we go above and beyond mere data and system protection – we provide you with peace of mind. Our comprehensive range of services includes Managed Cyber Security Services, Cyber Security Consulting, Cyber Security Risk Analysis, Cyber Security Defense Services, Security Incident Response, and more. By harnessing cutting-edge solutions and leveraging our expertise, we empower you to fortify your web applications and minimize vulnerability to attacks.
Don’t wait to secure your business. Get in touch with us today and discover how Purple Shield Security can revolutionize your cybersecurity defenses.
#cybersecuritynews #securitynews #hacking #datasecurity #cyberprotection #malware #cybersecurityconsulting #cybersecurityservices #ransomware

