Overview of BadSpace Malware
BadSpace is a sophisticated Windows backdoor malware that attackers deliver through compromised websites, especially those built on WordPress. This malware uses a multi-stage attack chain involving infected websites, command-and-control (C2) servers, fake browser updates, and a JScript downloader to infiltrate victims’ systems.
Infection Chain: How BadSpace Infiltrates Systems
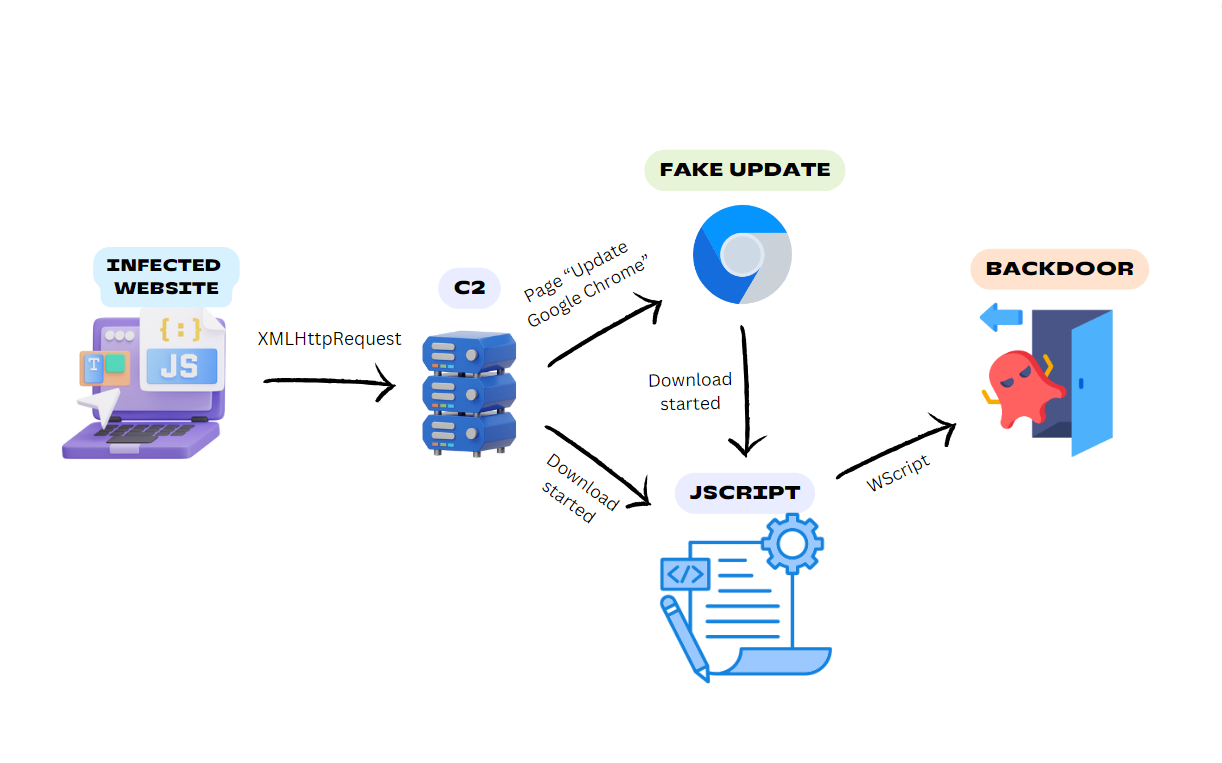
According to German cybersecurity company G DATA, BadSpace uses a multi-stage attack chain that begins with legitimate but compromised websites. These sites, often built on platforms like WordPress, are manipulated to deliver malware under the guise of fake browser updates. Details of the malware were first shared by researchers kevross33 and Gi7w0rm last month. The infection process follows these steps:
- Compromised Websites: The attack starts with an infected website that checks if the user is visiting for the first time. This is achieved by setting a cookie that tracks user visits.
- Data Collection: On the first visit, the website collects device information, including IP address, user-agent, and location, and sends this data to a hardcoded domain via an HTTP GET request.
- Fake Updates: The server response overlays the original webpage with a fake Google Chrome update pop-up. This pop-up either directly drops the malware or a JScript downloader that subsequently downloads and executes BadSpace.
Malware Delivery
BadSpace is typically delivered via high-ranking infected websites to leverage their credibility and large user base. These infected sites often inject malicious code into JavaScript libraries or the index pages. The JScript files used in the attack employ various obfuscation techniques to evade detection. The JScript downloader sometimes uses extension spoofing, such as “.pdf.js”, to disguise its true nature.
Technical Details
Anti-Sandbox Techniques: BadSpace employs several anti-sandbox checks, including:
- Counting the number of folders in %TEMP% and %APPDATA%.
- Querying the registry for “DisplayName” subkeys under SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall.
- Checking the number of processors and global memory status.
Persistence Mechanisms: After bypassing sandbox checks, BadSpace creates a mutex with a unique UUID and sets up persistence using scheduled tasks. For DLL files, it uses the command:
Rundll32.exe %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\RtlUpd\RtlUpd.dllStart /p
If this fails, it tries a different folder:
Rundll32.exe %APPDATA%\RtlUpd\RtlUpd.dllStart /p
C2 Communication: BadSpace uses a hardcoded RC4 key to encrypt communication with its C2 server. The initial request sends a cookie containing encrypted system information, such as computer name, DNS domain, volume serial number hash, OS version, and username.
String and API Obfuscation: The malware’s strings and API names are encrypted with RC4. Each string blob includes four bytes of encrypted data length, four bytes of the RC4 key, and the encrypted data. APIs are resolved dynamically using LoadLibraryW and GetProcAddress.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
JavaScript Infections:
- 2b4d7ed8d12d34cbf5d57811ce32f9072845f5274a2934221dd53421c7b8762b
- f3fed82131853a35ebb0060cb364c89f42f55e357099289ca22f7af651ee2c48
JScript Droppers:
- c64cb9e0740c17b2561eed963a4d9cf452e84f462d5004ddbd0e0c021a8fdabc
- 9786569f7c5e5183f98986b78b8e6d7afcad78329c9e61fb881d3d0960bc6a15
BadSpace Backdoor Samples:
- 6a195e6111c9a4b8c874d51937b53cd5b4b78efc32f7bb255012d05087586d8f
- 2a5a12cc4ef2f0f527cc072243aa27d3e95e48402ef674e92c6709dc03a0836a
C2 Domains:
- uhsee[.]com
- kongtuke[.]com
C2 IPs:
- 80.66.88.146
- 185.49.69.41
Conclusion
BadSpace is a highly evasive and persistent malware that poses significant threats by exploiting legitimate but compromised websites. It uses sophisticated obfuscation and anti-sandbox techniques to evade detection and maintain persistence on infected systems. Organizations must stay informed about such threats and collaborate with cybersecurity firms to implement effective defense strategies. By monitoring IoCs and employing advanced detection techniques, organizations can collectively enhance their cybersecurity posture and mitigate the risks posed by malware like BadSpace.
For more detailed insights and personalized cybersecurity solutions, contact our cybersecurity experts today.