A malicious crypto mining campaign codenamed ‘REF4578,’ has been discovered deploying a malicious payload named GhostEngine that uses vulnerable drivers to turn off security products and deploy an XMRig miner. Researchers at the cybersecurity firms Elastic Security Labs and Antiy have underlined the unusual sophistication of these crypto-mining attacks in separate reports and shared detection rules to help defenders identify and stop them. However, neither report attributes the activity to known threat actors nor shares details about targets/victims, so the campaign’s origin and scope remain unknown.
GhostEngine Overview
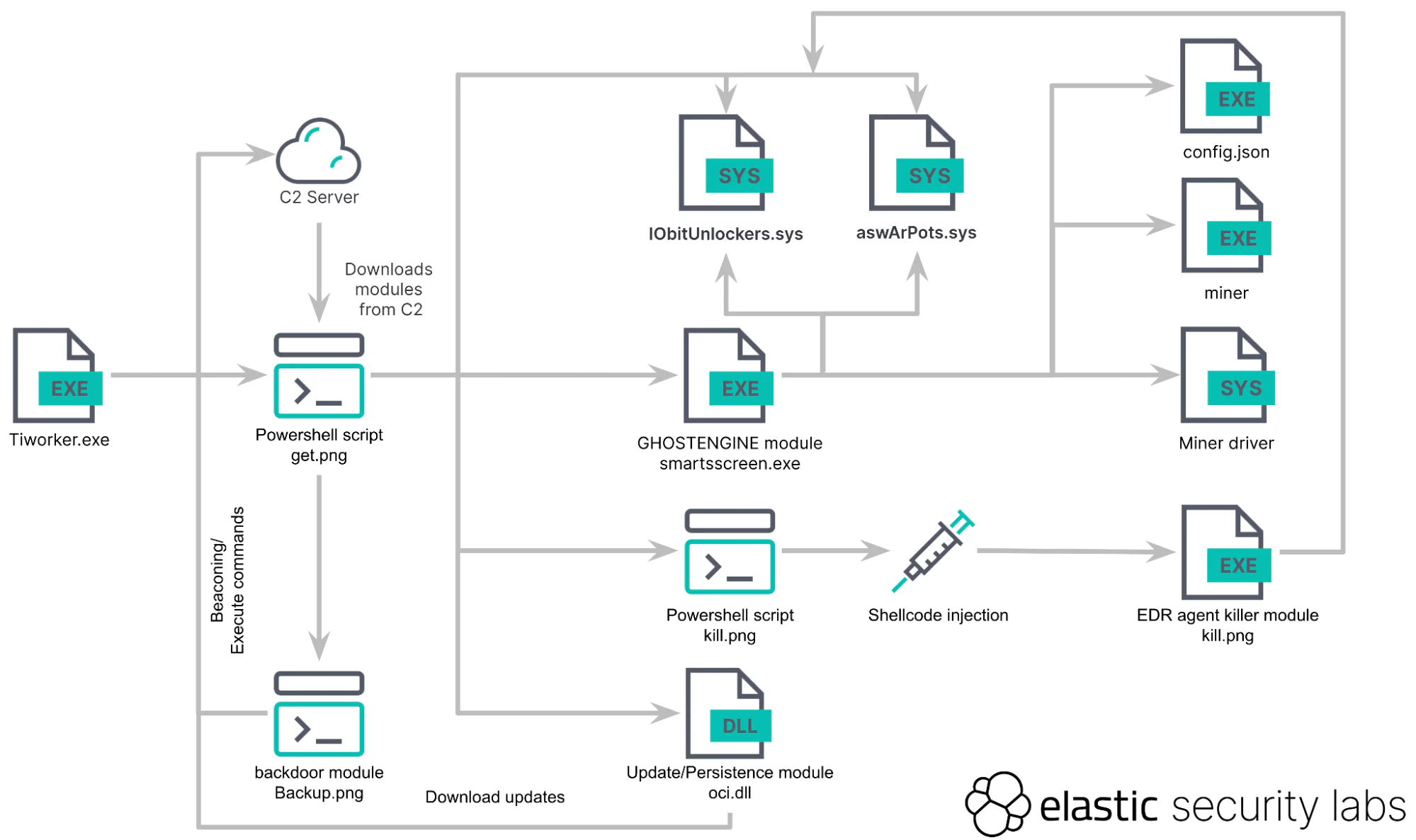
GhostEngine is a multimodule malware designed to perform several malicious activities on an infected system. The attack vector starts with the execution of a malicious file named ‘Tiworker.exe,’ which masquerades as a legitimate Windows file. This executable is the initial staging payload for GhostEngine, a PowerShell script that downloads various modules to conduct different behaviors on an infected device.
Initial Infection and Payload Delivery
When Tiworker.exe is executed, it will download a PowerShell script named ‘get.png’ from the attacker’s command and control (C2) server, which acts as GhostEngine’s primary loader. This PowerShell script downloads additional modules and their configurations, disables Windows Defender, enables remote services, and clears various Windows event logs.
Next, get.png verifies that the system has at least 10MB of free space, which is necessary for furthering the infection, and creates scheduled tasks named ‘OneDriveCloudSync,’ ‘DefaultBrowserUpdate,’ and ‘OneDriveCloudBackup,’ for persistence. The PowerShell script will then download and launch an executable named smartsscreen.exe, which acts as GhostEngine’s primary payload.
Main Functions and Modules
- Persistence and Evasion:
- GhostEngine uses various tactics to ensure persistence on the infected system. It creates scheduled tasks to maintain its presence even after system reboots.
- The malware disables Windows Defender and clears Windows event logs to evade detection.
- Driver Exploitation:
- To terminate Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) software, GhostEngine loads two vulnerable kernel drivers: aswArPots.sys (Avast driver), which is used to terminate EDR processes, and IObitUnlockers.sys (Iobit driver) to delete the affected files.
- Cryptocurrency Mining:
- GhostEngine downloads and launches XMRig, a legitimate application used for mining the Monero cryptocurrency. This process involves significant computational resources, which can degrade the performance of the infected system.
- Backdoor Capabilities:
- GhostEngine includes a backdoor component, enabling attackers to download and execute additional malware. This allows the threat actor to maintain control over the compromised system and deploy further malicious payloads as needed.
Detection and Mitigation
Researchers have provided detection rules and guidelines to help defenders identify and stop the GhostEngine malware. It is crucial for organizations to implement these measures and stay vigilant against such sophisticated attacks.
Detection rules and behavior prevention events associated with the campaign include the following:
- Suspicious PowerShell downloads
- Service control spawned via Script Interpreter
- Local scheduled task creation
- Process execution from an unusual directory
- Unusual parent-child relationship
- Clearing Windows event logs
- Tampering with Microsoft Windows Defender
Recommendations
- Regular Security Updates
- Patch Management: Ensure all operating systems, applications, and security software are regularly updated with the latest patches and versions. This reduces the risk of vulnerabilities being exploited by malware.
- Automated Updates: Where possible, enable automated updates to ensure timely application of critical patches without manual intervention.
- Network Traffic Monitoring
- Anomaly Detection: Implement network monitoring tools that can detect unusual traffic patterns indicative of malware activity. Anomaly-based detection can identify deviations from normal network behavior.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Deploy IDS to monitor network traffic for malicious activity and policy violations. Ensure the IDS is configured to detect advanced threats like GhostEngine.
- Advanced Threat Detection
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR): Utilize XDR solutions that provide real-time monitoring and detection of endpoint threats. Ensure the XDR is capable of detecting and responding to sophisticated attacks like those employing vulnerable drivers.
- Behavioral Analysis: Implement security tools that use behavioral analysis to identify malicious activities based on the behavior of applications and processes rather than relying solely on signature-based detection.
- Threat Intelligence
- Threat Intelligence Feeds: Subscribe to threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about the latest threats, vulnerabilities, and attack vectors.
Conclusion
The REF4578 crypto mining campaign, with its GhostEngine payload, represents a significant threat due to its sophisticated attack chain and use of multiple techniques to evade detection. By implementing these extended recommendations with the assistance of a reputable cybersecurity firm or cybersecurity consultant, organizations can significantly enhance their ability to detect, prevent, and respond to sophisticated cyber threats like the REF4578 campaign and GhostEngine malware. Engaging in proactive cybersecurity services and staying aware is key to maintaining a robust cybersecurity posture.